ONDC stands for the “Open Network for Digital Commerce.” It is an initiative introduced by the Indian government to create a unified and standardised digital commerce infrastructure in India. The main goal of ONDC is to promote fair competition, transparency, and innovation in the digital commerce sector.
How ONDC Works?
Imagine a marketplace where buyers and sellers come to transact. Every buyer has a different preferred application while sellers themselves are separate entities. ONDC is the common gateway that will connect them. In fact, ONDC will function as a link which will connect those buyers and sellers to each other, aiding with price discovery, accessibility, locations, product choices, etc.
Buyer platforms will be responsible for buyers’ choices from different areas. Buyers can easily log in and search for their desired products. Seller platforms are accountable for onboarding merchants and listing their products. The merchants will be accountable for logistics and operations.
To summarise, ONDC is a network that acts as a gateway, where buyers and sellers from different platforms will have an integrated connection to exchange goods and services.
ONDC Vs Marketplace
One must have used e-commerce platforms such as Amazon or Flipkart. These platforms onboard sellers, merchants, and other partners who have various products to offer to consumers.
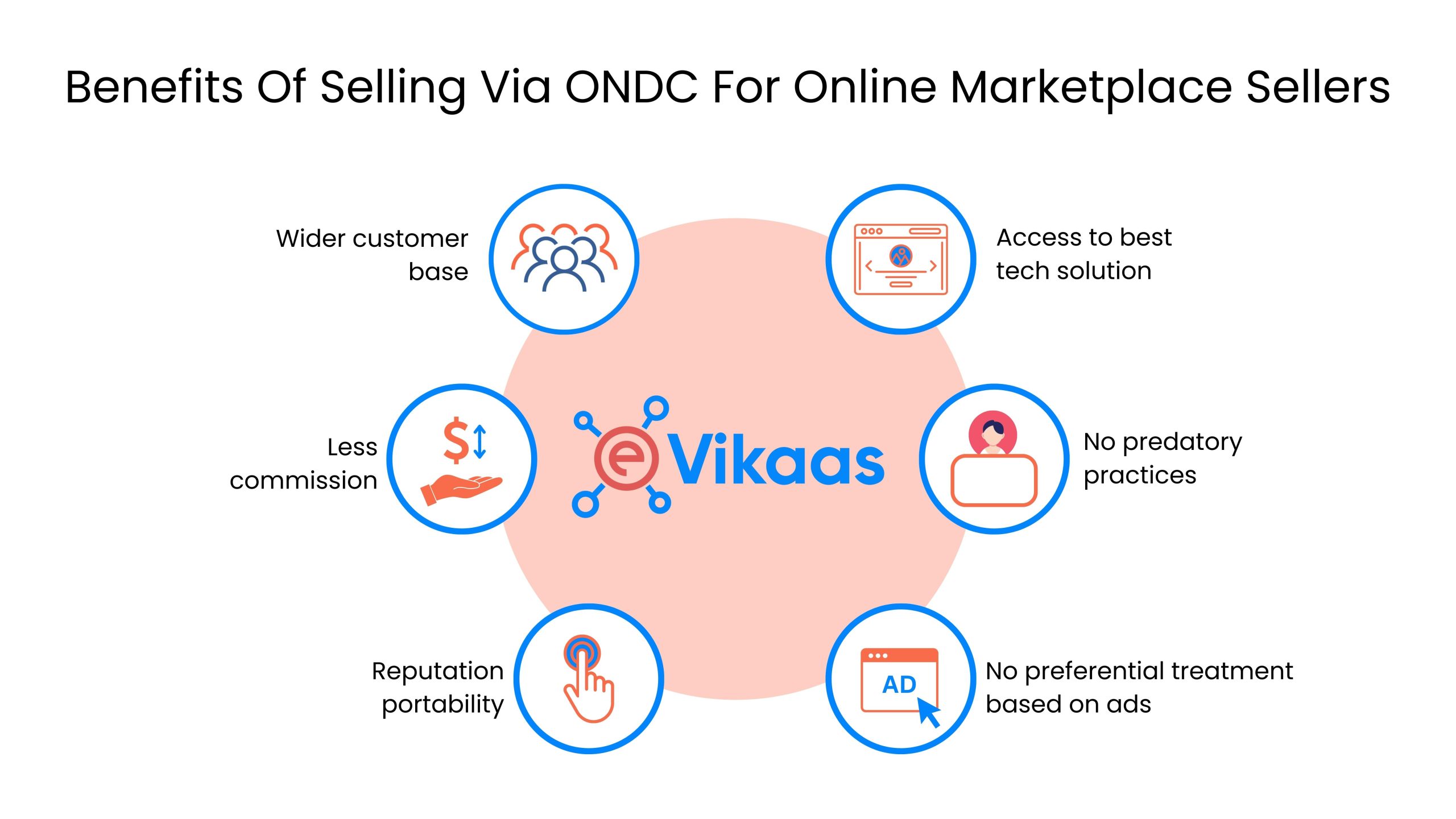
Sellers may have to pay a commission to e-commerce platforms while buyers have to pay delivery fees or subscription fees. While medium to large retailers may not have a problem with the commissions, small enterprises have to forfeit a large chunk of their margin.
Based on the ideology of ONDC, it has the potential to level the playing field by allowing small retailers to sell groceries, clothes, or other utility businesses and host their products.
The government claims that the merchants can get on boarded to the ONDC platform at charges as low as Rs 2000 which is a drop in the ocean to the hefty commission and onboarding fees charged by major marketplaces.
The platform hosts both buyer and seller apps, whereas Amazon and Flipkart are both sellers’ and buyers’ platforms in one place. If the project is successful, many retailers will have the opportunity to sell their products online and be a part of the overall ecosystem.
Accessing ONDC
It is evident now that ONDC links both buyer and seller apps to connect potential buyers and sellers. If somebody wishes to order anything from ONDC, he/she can download any of the buyer’s applications such as Paytm, Pincode, Meesho, Magicpin, etc.

These apps have an ONDC ecosystem built into them. For example: If you search ‘ONDC’ in Meesho, it will bring you to the ONDC network and allow you to browse products.
There are also seller applications such as Unizap, Mystore, eSamudaay, etc. which enables sellers to list their products and the ONDC network helps to connect them with prospective buyers.
ONDC and the Future of E-commerce in India
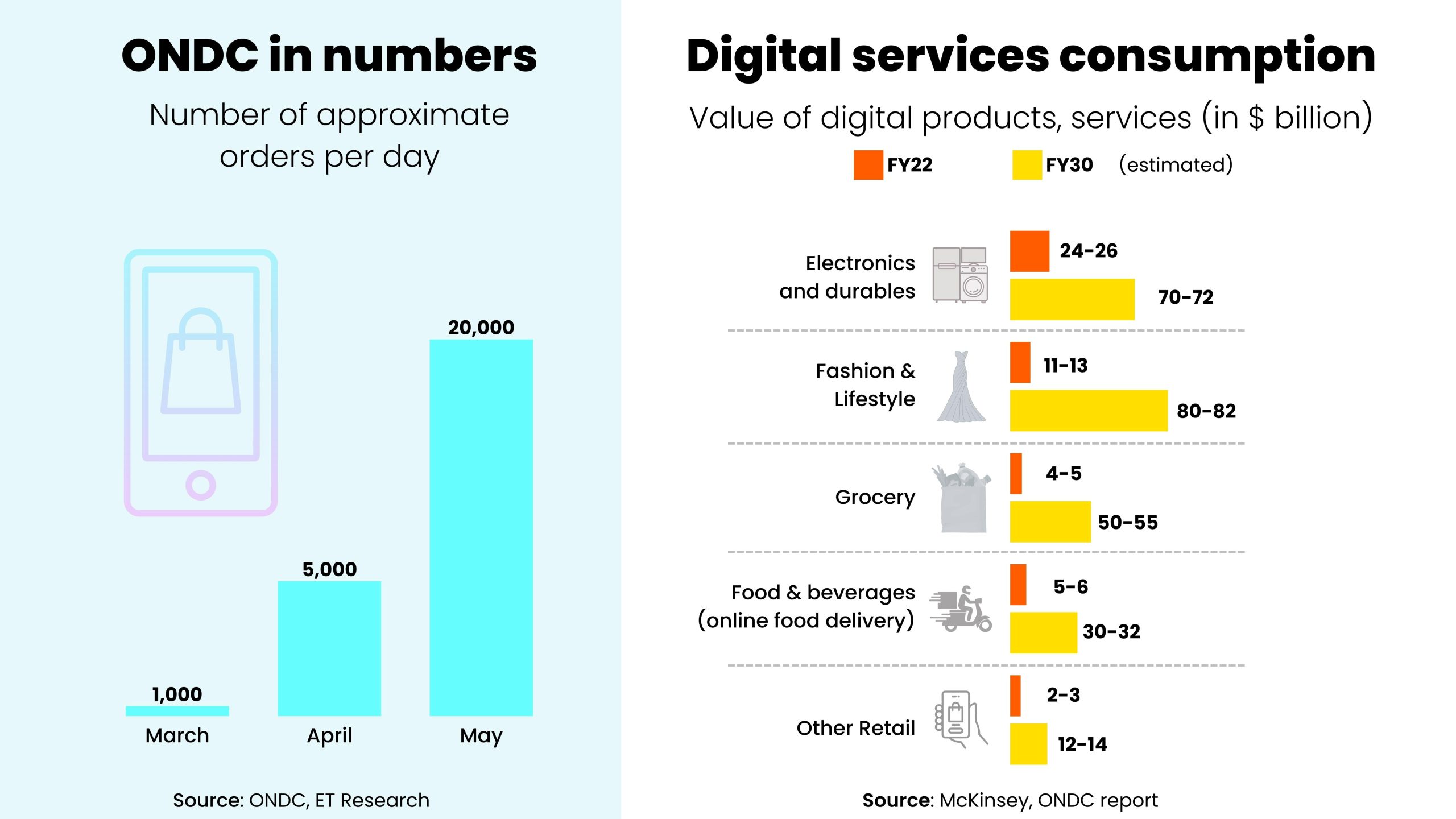
Even though ONDC has started in an optimistic manner with daily orders crossing 35,000 daily and aims at 2,00,000 transactions by year end, there lies a lot of manual work to be done to transform the e-commerce space in India.
The platform boasts less commissions compared to other marketplaces and hence, buyers and sellers see incredible potential. But, it remains to be seen how long this can be sustained.
If the platform is victorious in building the ecosystem and the technology, it can help MSME’s to grow and increase the overall productivity of the country. This will also be beneficial for customers as they have to pay lesser charges.
Now, in its initial days, the government is also evaluating various strategies and looking to capitalize on the great opportunity. However, the future seems promising for ONDC, as it did with UPI.
ONDC AND ITS NEED IN INDIA:
The Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC) is an initiative in India aimed at creating a unified and standardised digital commerce infrastructure. The need for ONDC in India can be understood by examining the challenges and objectives it addresses:
- Promoting Fair Competition: The Indian e-commerce sector has been controlled by a few major players that can suppress competition. ONDC aims to create a level playing field by allowing smaller businesses and startups to participate more effectively in digital commerce.
- Standardisation: ONDC seeks to establish common standards and protocols for digital commerce, making it easier for various players, including retailers, service providers, and consumers, to interact seamlessly in the digital ecosystem.
- Interoperability: The digital commerce landscape in India is disintegrated with different platforms and systems not always compatible with each other. ONDC aims to ensure interoperability between various digital commerce platforms, making it easier for consumers to switch between services and access a wider range of products and services.
- Data Ownership and Privacy: ONDC aims at giving consumers greater control over their data and ensuring their data privacy. It promotes data portability, allowing consumers to move their data between service providers while maintaining ownership and control.
- Innovation and Entrepreneurship: By lowering restrictions on entry barriers and promoting competition, ONDC encourages innovation and entrepreneurship in the digital commerce sector. This leads to the development of new business models, technologies, and services.
- Government Initiatives: ONDC positions with the Indian government’s Digital India and Atmanirbhar Bharat (self-reliant India) initiatives, which aims to promote digitalization and self-sufficiency in various sectors, including commerce.
- Consumer Choice: ONDC aims to empower consumers by providing them with a wider range of choices and access to a variety of products and services through different platforms.
Economic Growth: A well-regulated and competitive digital commerce ecosystem can contribute significantly to India’s economic growth by boosting online sales, creating jobs, and increasing tax revenues.
In summary, ONDC addresses the requirement for a more transparent, competitive, and standardised digital commerce ecosystem in India. It aims to empower both consumers and businesses while promoting innovation and economic growth in the sector.

ONDC AND ITS BENEFITS TO INDIAN BUYERS AND SELLERS:
The Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC) in India is designed to benefit various stakeholders in the digital commerce ecosystem, including:
- Consumers: ONDC aims to empower consumers by giving them more control over their data, ensuring data privacy, and providing them with more choices and options when shopping online. It allows consumers to switch between digital commerce platforms easily and access a wider range of products and services.
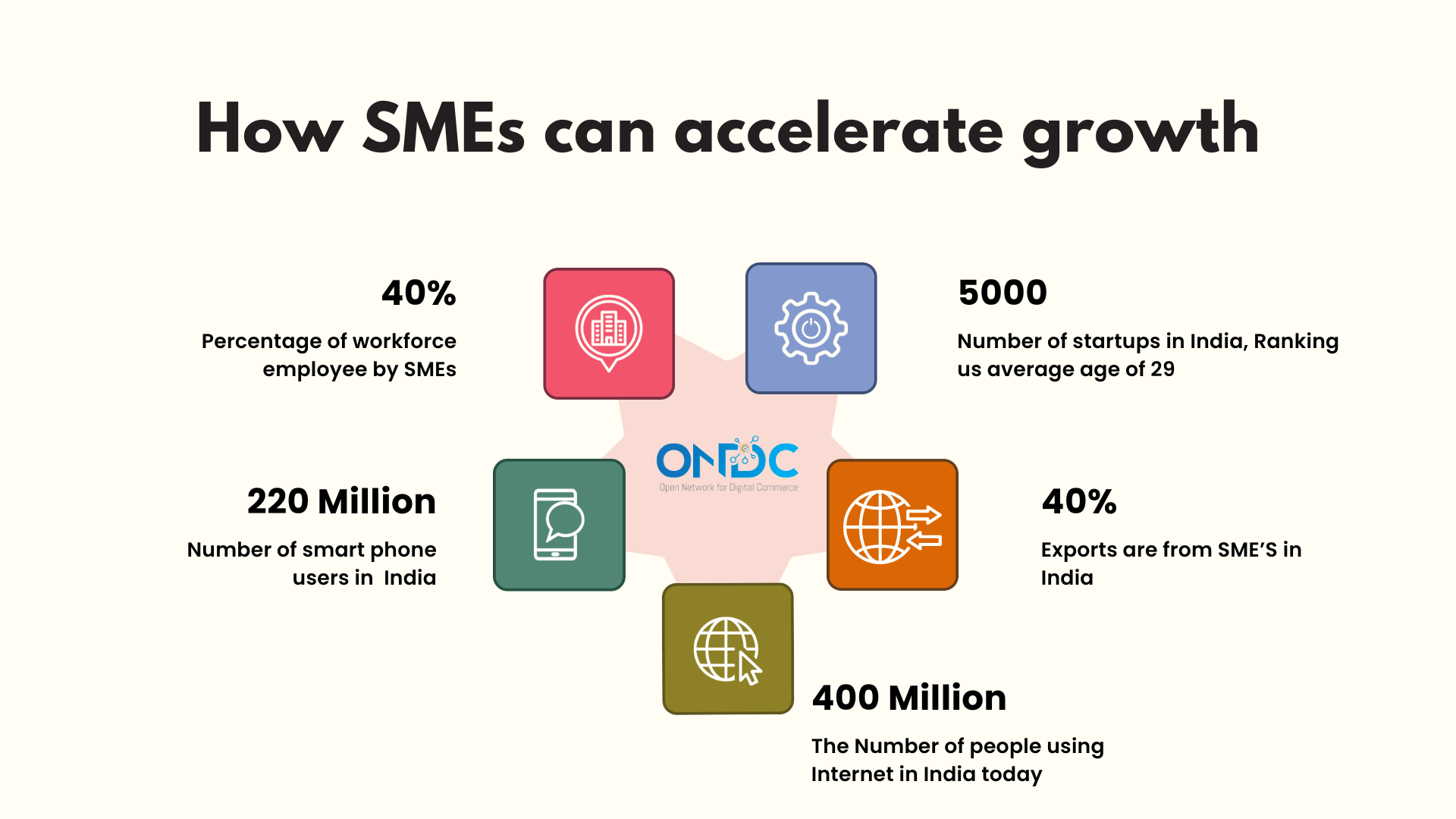
- Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs): SMEs often face challenges when competing with larger e-commerce players. ONDC provides SMEs with a level playing field by reducing entry barriers, ensuring fair competition, and enabling them to reach a broader customer base through digital channels.
- Startups: ONDC aims to increase innovation and entrepreneurship in the digital commerce sector by lowering barriers to entry and creating a more competitive environment. Startups can leverage standardised infrastructure and access a larger market through ONDC.
- Digital Commerce Service Providers: Companies providing digital commerce services, such as payment gateways, logistics providers, and online marketplaces, can benefit from ONDC by having access to a standardised and interoperable ecosystem, potentially increasing their customer base.
- Government: The Indian government aims to benefit from ONDC by aligning it with its Digital India and Atmanirbhar Bharat initiatives, which aims to promote digitalization, self-reliance, and economic growth. ONDC can contribute to these goals by boosting online sales, creating jobs, and increasing tax revenues.
- Regulators: Regulators benefit from ONDC by having a standardised framework for overseeing digital commerce activities, ensuring data privacy and security, and promoting fair competition. This can make it easier to regulate and monitor the industry effectively.
- Consumers’ Rights and Privacy Advocates: ONDC places a strong emphasis on data ownership and privacy, which can be seen as a benefit by advocates for consumer rights and privacy protection.
- Overall Economy: A well-regulated and competitive digital commerce ecosystem, facilitated by ONDC, can add to the growth of the Indian economy by stimulating economic activity, increasing employment opportunities, and generating tax revenue.
While ONDC has the potential to benefit a wide range of stakeholders, its success in doing so will depend on effective implementation, adoption by market players, and ongoing support from the government and regulators.
Is ONDC for Small Or Large Enterprises?
The Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC) in India is designed to benefit both small and large enterprises in the digital commerce ecosystem. It aims to create a more inclusive and competitive environment that can accommodate a wide range of businesses, regardless of their size. Here’s how ONDC can benefit both small and large enterprises:
- Small Enterprises (SMEs):
Reduced Entry Barriers: ONDC seeks to lower entry barriers for SMEs, making it hassle-free for them to participate in the digital commerce space. SMEs can then set up their online stores and sell their products or services more easily.
Access to a Larger Market: By providing standardised infrastructure and interoperability, ONDC can help SMEs reach a broader customer base, potentially expanding their market presence beyond their immediate geographical area.
Fair Competition: ONDC aims to promote fair competition, ensuring that SMEs can compete on a level playing field with larger e-commerce players.
Innovation Opportunities: SMEs and startups can innovate and create unique offerings within the ONDC ecosystem, benefiting from the standardised infrastructure while differentiating themselves in the market.
- Large Enterprises:
- Standardisation and Interoperability: Large enterprises can benefit from ONDC by leveraging standardised infrastructure and protocols. This can lead to greater efficiency in their digital commerce operations and the ability to effortlessly integrate with other platforms and services.
- Compliance and Regulation: ONDC provides a framework that helps large enterprises comply with regulations and standards in the digital commerce sector. It simplifies regulatory compliance and reporting.
- Market Expansion: Large enterprises can use ONDC to reach a larger and diverse audience and potentially explore new market segments or regions, thus expanding their market presence.
- Data Portability: ONDC’s emphasis on data ownership and portability benefits both consumers and businesses. Large enterprises can ensure data portability while maintaining consumer trust.
In summary, ONDC is designed to benefit businesses of all sizes in the digital commerce sector. Small enterprises, in particular, can benefit from the lowered barriers to entry and improved market access, while large enterprises can benefit from standardized infrastructure and compliance support. The goal is to create a more competitive and inclusive digital commerce ecosystem in India.
ONDC’s Aid In Ecommerce Penetration:
The Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC) in India is expected to help boost e-commerce growth and penetration in several ways:
- Lower Entry Barriers: ONDC aims to reduce entry barriers for businesses, particularly small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). This means more businesses can set up their online stores and participate in e-commerce, increasing the number of sellers in the market.
- Interoperability: ONDC promotes interoperability among different e-commerce platforms and services. This means that consumers can switch between platforms more easily and access a broader range of products and services. This increased convenience can encourage more people to shop online.
- Data Ownership and Portability: ONDC emphasizes data ownership and portability. Consumers can have more control over their data and can choose to move it between service providers, enhancing trust and confidence in online transactions.
- Standardization: By creating common standards and protocols, ONDC streamlines various processes in e-commerce, from payment gateways to logistics. This efficiency can lead to smoother and more reliable online shopping experiences, encouraging consumers to shop online more frequently.
- Innovation: ONDC’s standardized infrastructure can foster innovation within the e-commerce sector. New players, including start-ups, can enter the market with innovative solutions, leading to the development of new technologies and business models that attract more consumers.
- Increased Competition: ONDC promotes fair competition in the e-commerce space. This competition can lead to lower prices, better deals, and improved customer service, all of which make online shopping more attractive to consumers.
Overall, ONDC aims to create a more transparent, efficient, and consumer-friendly digital commerce ecosystem in India. By addressing these key aspects and promoting a competitive environment, it is expected to contribute significantly to the growth and penetration of e-commerce in the country.

Conclusion
By now ONDC’s meaning must have been clear and you also know how ONDC works. The government has established this platform as a catalyst to empower small businesses to transform them into diversified opportunities for buyers and sellers.
ONDC is a government-backed digital commerce network launched in India. Its core objective is to diminish the market dominance of two major e-commerce players and ensure a level playing field for all sellers and dealers. Operating on a network-centric model, ONDC will establish connections among sellers, buyers, and delivery partners across various platforms, thereby expanding the choices available to all participants.
ONDC stands for the “Open Network for Digital Commerce.” It is an initiative introduced by the Indian government to create a unified and standardised digital commerce infrastructure in India. The main goal of ONDC is to promote fair competition, transparency, and innovation in the digital commerce sector.

How ONDC Works?
Imagine a marketplace where buyers and sellers come to transact. Every buyer has a different preferred application while sellers themselves are separate entities. ONDC is the common gateway that will connect them. In fact, ONDC will function as a link which will connect those buyers and sellers to each other, aiding with price discovery, accessibility, locations, product choices, etc.
Buyer platforms will be responsible for buyers’ choices from different areas. Buyers can easily log in and search for their desired products. Seller platforms are accountable for onboarding merchants and listing their products. The merchants will be accountable for logistics and operations.
To summarise, ONDC is a network that acts as a gateway, where buyers and sellers from different platforms will have an integrated connection to exchange goods and services.
ONDC Vs Marketplace
One must have used e-commerce platforms such as Amazon or Flipkart. These platforms onboard sellers, merchants, and other partners who have various products to offer to consumers.
Sellers may have to pay a commission to e-commerce platforms while buyers have to pay delivery fees or subscription fees. While medium to large retailers may not have a problem with the commissions, small enterprises have to forfeit a large chunk of their margin.
Based on the ideology of ONDC, it has the potential to level the playing field by allowing small retailers to sell groceries, clothes, or other utility businesses and host their products.
The government claims that the merchants can get on boarded to the ONDC platform at charges as low as Rs 2000 which is a drop in the ocean to the hefty commission and onboarding fees charged by major marketplaces.
The platform hosts both buyer and seller apps, whereas Amazon and Flipkart are both sellers’ and buyers’ platforms in one place. If the project is successful, many retailers will have the opportunity to sell their products online and be a part of the overall ecosystem.
Accessing ONDC
It is evident now that ONDC links both buyer and seller apps to connect potential buyers and sellers. If somebody wishes to order anything from ONDC, he/she can download any of the buyer’s applications such as Paytm, Pincode, Meesho, Magicpin, etc.

These apps have an ONDC ecosystem built into them. For example: If you search ‘ONDC’ in Meesho, it will bring you to the ONDC network and allow you to browse products.
There are also seller applications such as Unizap, Mystore, eSamudaay, etc. which enables sellers to list their products and the ONDC network helps to connect them with prospective buyers.
ONDC and the Future of E-commerce in India
Even though ONDC has started in an optimistic manner with daily orders crossing 35,000 daily and aims at 2,00,000 transactions by year end, there lies a lot of manual work to be done to transform the e-commerce space in India.
The platform boasts less commissions compared to other marketplaces and hence, buyers and sellers see incredible potential. But, it remains to be seen how long this can be sustained.

If the platform is victorious in building the ecosystem and the technology, it can help MSME’s to grow and increase the overall productivity of the country. This will also be beneficial for customers as they have to pay lesser charges.
Now, in its initial days, the government is also evaluating various strategies and looking to capitalize on the great opportunity. However, the future seems promising for ONDC, as it did with UPI.
ONDC AND ITS NEED IN INDIA:
The Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC) is an initiative in India aimed at creating a unified and standardised digital commerce infrastructure. The need for ONDC in India can be understood by examining the challenges and objectives it addresses:
- Promoting Fair Competition: The Indian e-commerce sector has been controlled by a few major players that can suppress competition. ONDC aims to create a level playing field by allowing smaller businesses and startups to participate more effectively in digital commerce.
- Standardisation: ONDC seeks to establish common standards and protocols for digital commerce, making it easier for various players, including retailers, service providers, and consumers, to interact seamlessly in the digital ecosystem.
- Interoperability: The digital commerce landscape in India is disintegrated with different platforms and systems not always compatible with each other. ONDC aims to ensure interoperability between various digital commerce platforms, making it easier for consumers to switch between services and access a wider range of products and services.
- Data Ownership and Privacy: ONDC aims at giving consumers greater control over their data and ensuring their data privacy. It promotes data portability, allowing consumers to move their data between service providers while maintaining ownership and control.
- Innovation and Entrepreneurship: By lowering restrictions on entry barriers and promoting competition, ONDC encourages innovation and entrepreneurship in the digital commerce sector. This leads to the development of new business models, technologies, and services.
- Government Initiatives: ONDC positions with the Indian government’s Digital India and Atmanirbhar Bharat (self-reliant India) initiatives, which aims to promote digitalization and self-sufficiency in various sectors, including commerce.
- Consumer Choice: ONDC aims to empower consumers by providing them with a wider range of choices and access to a variety of products and services through different platforms.
Economic Growth: A well-regulated and competitive digital commerce ecosystem can contribute significantly to India’s economic growth by boosting online sales, creating jobs, and increasing tax revenues.
In summary, ONDC addresses the requirement for a more transparent, competitive, and standardised digital commerce ecosystem in India. It aims to empower both consumers and businesses while promoting innovation and economic growth in the sector.

ONDC AND ITS BENEFITS TO INDIAN BUYERS AND SELLERS:
The Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC) in India is designed to benefit various stakeholders in the digital commerce ecosystem, including:
- Consumers: ONDC aims to empower consumers by giving them more control over their data, ensuring data privacy, and providing them with more choices and options when shopping online. It allows consumers to switch between digital commerce platforms easily and access a wider range of products and services.
- Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs): SMEs often face challenges when competing with larger e-commerce players. ONDC provides SMEs with a level playing field by reducing entry barriers, ensuring fair competition, and enabling them to reach a broader customer base through digital channels.
- Startups: ONDC aims to increase innovation and entrepreneurship in the digital commerce sector by lowering barriers to entry and creating a more competitive environment. Startups can leverage standardised infrastructure and access a larger market through ONDC.
- Digital Commerce Service Providers: Companies providing digital commerce services, such as payment gateways, logistics providers, and online marketplaces, can benefit from ONDC by having access to a standardised and interoperable ecosystem, potentially increasing their customer base.
- Government: The Indian government aims to benefit from ONDC by aligning it with its Digital India and Atmanirbhar Bharat initiatives, which aims to promote digitalization, self-reliance, and economic growth. ONDC can contribute to these goals by boosting online sales, creating jobs, and increasing tax revenues.
- Regulators: Regulators benefit from ONDC by having a standardised framework for overseeing digital commerce activities, ensuring data privacy and security, and promoting fair competition. This can make it easier to regulate and monitor the industry effectively.
- Consumers’ Rights and Privacy Advocates: ONDC places a strong emphasis on data ownership and privacy, which can be seen as a benefit by advocates for consumer rights and privacy protection.
- Overall Economy: A well-regulated and competitive digital commerce ecosystem, facilitated by ONDC, can add to the growth of the Indian economy by stimulating economic activity, increasing employment opportunities, and generating tax revenue.
While ONDC has the potential to benefit a wide range of stakeholders, its success in doing so will depend on effective implementation, adoption by market players, and ongoing support from the government and regulators.
Is ONDC for Small Or Large Enterprises?
The Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC) in India is designed to benefit both small and large enterprises in the digital commerce ecosystem. It aims to create a more inclusive and competitive environment that can accommodate a wide range of businesses, regardless of their size. Here’s how ONDC can benefit both small and large enterprises:
- Small Enterprises (SMEs):
Reduced Entry Barriers: ONDC seeks to lower entry barriers for SMEs, making it hassle-free for them to participate in the digital commerce space. SMEs can then set up their online stores and sell their products or services more easily.
Access to a Larger Market: By providing standardised infrastructure and interoperability, ONDC can help SMEs reach a broader customer base, potentially expanding their market presence beyond their immediate geographical area.
Fair Competition: ONDC aims to promote fair competition, ensuring that SMEs can compete on a level playing field with larger e-commerce players.
Innovation Opportunities: SMEs and startups can innovate and create unique offerings within the ONDC ecosystem, benefiting from the standardised infrastructure while differentiating themselves in the market.

- Large Enterprises:
- Standardisation and Interoperability: Large enterprises can benefit from ONDC by leveraging standardised infrastructure and protocols. This can lead to greater efficiency in their digital commerce operations and the ability to effortlessly integrate with other platforms and services.
- Compliance and Regulation: ONDC provides a framework that helps large enterprises comply with regulations and standards in the digital commerce sector. It simplifies regulatory compliance and reporting.
- Market Expansion: Large enterprises can use ONDC to reach a larger and diverse audience and potentially explore new market segments or regions, thus expanding their market presence.
- Data Portability: ONDC’s emphasis on data ownership and portability benefits both consumers and businesses. Large enterprises can ensure data portability while maintaining consumer trust.
In summary, ONDC is designed to benefit businesses of all sizes in the digital commerce sector. Small enterprises, in particular, can benefit from the lowered barriers to entry and improved market access, while large enterprises can benefit from standardized infrastructure and compliance support. The goal is to create a more competitive and inclusive digital commerce ecosystem in India.
ONDC’s Aid In Ecommerce Penetration:
The Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC) in India is expected to help boost e-commerce growth and penetration in several ways:
- Lower Entry Barriers: ONDC aims to reduce entry barriers for businesses, particularly small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). This means more businesses can set up their online stores and participate in e-commerce, increasing the number of sellers in the market.
- Interoperability: ONDC promotes interoperability among different e-commerce platforms and services. This means that consumers can switch between platforms more easily and access a broader range of products and services. This increased convenience can encourage more people to shop online.
- Data Ownership and Portability: ONDC emphasizes data ownership and portability. Consumers can have more control over their data and can choose to move it between service providers, enhancing trust and confidence in online transactions.
- Standardization: By creating common standards and protocols, ONDC streamlines various processes in e-commerce, from payment gateways to logistics. This efficiency can lead to smoother and more reliable online shopping experiences, encouraging consumers to shop online more frequently.
- Innovation: ONDC’s standardized infrastructure can foster innovation within the e-commerce sector. New players, including start-ups, can enter the market with innovative solutions, leading to the development of new technologies and business models that attract more consumers.
- Increased Competition: ONDC promotes fair competition in the e-commerce space. This competition can lead to lower prices, better deals, and improved customer service, all of which make online shopping more attractive to consumers.
Overall, ONDC aims to create a more transparent, efficient, and consumer-friendly digital commerce ecosystem in India. By addressing these key aspects and promoting a competitive environment, it is expected to contribute significantly to the growth and penetration of e-commerce in the country.

Conclusion
By now ONDC’s meaning must have been clear and you also know how ONDC works. The government has established this platform as a catalyst to empower small businesses to transform them into diversified opportunities for buyers and sellers.
ONDC is a government-backed digital commerce network launched in India. Its core objective is to diminish the market dominance of two major e-commerce players and ensure a level playing field for all sellers and dealers. Operating on a network-centric model, ONDC will establish connections among sellers, buyers, and delivery partners across various platforms, thereby expanding the choices available to all participants.







